5G-Mobile Network Solution

5th generation mobile network (5G) is new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G networks. 5G is designed to connect everyone and everything together including machines, objects and devices. 5G provides higher speeds, ultra low latency, more reliability and massive network capacity.
The ITU-R has defined three main application areas for the enhanced capabilities of 5G. They are Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC) and Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC). eMBB uses 5G as a progression from 4G LTE mobile broadband services, with faster connections, higher throughput and more capacity. URLLC uses the network for mission critical applications that require uninterrupted and robust data exchange.mMTC is used to connect to a large number of devices. It is also called massive machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. This communication link is designed for IoT services.
5G NR (new radio) includes lower frequencies (FR1), below 6 GHz, and higher frequencies (FR2), above 24 GHz, each with different capabilities.
FR1 frequency range (< 6 GHz)
The maximum channel bandwidth defined for FR1 is 100 MHz, due to the scarcity of continuous spectrum in this crowded frequency range. The band most widely being used for 5G in this range is 3.3–4.2 GHz. Low-band spectrum offers the farthest area coverage but is slower than the others.
FR2 frequency range (> 24 GHz)
The minimum channel bandwidth defined for FR2 is 50 MHz and the maximum is 400 MHz. 5G can use frequencies of up to 300 GHz. The higher the frequency, the greater the ability to support high data-transfer speeds.
Low-band spectrum (sub-1GHz) offers great coverage area and wall penetration. Drawback is peak data speeds top out around 100Mbps. Mid-band spectrum provides faster speeds and lower latency than low-band. But it failed to penetrate buildings as effectively as low-band spectrum. Expect peak speeds up to 1Gbps on mid-band spectrum.
High-band spectrum delivers the highest performance for 5G. It is often referred to as mmWave. High-band spectrum can offer peak speeds up to 10Gbps and has extremely low latency. The main drawback of high-band is low coverage area and building penetration is poor. That means that to create an effective high-band network, you’ll need a ton of cells.
The spectrum used by various 5G devices will be near passive remote sensing, such as by weather and Earth observation satellites. Interference will occur without effective controls. Interference to satellite operations impairs numerical weather prediction performance with substantially deleterious economic and public safety impacts in areas such as commercial aviation.
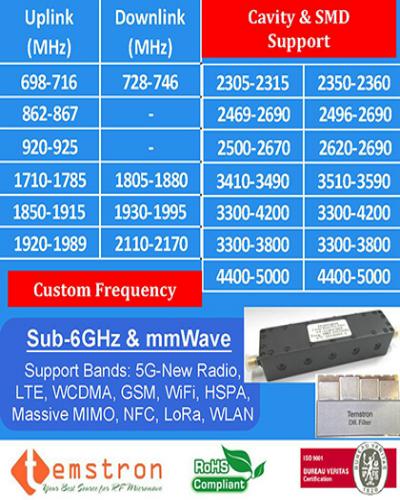 |
 |
Custom Solution:
Helical Filter
 |
Custom Support
|
Cavity Filter
 |
Custom Support
|
SMD Filter
 |
Custom Support
|

















